The hearing test is completely safe and harmless. Before the hearing test, a hearing prosthetic specialist briefly and understandably explains to the patient what to do during the test and how this test works.
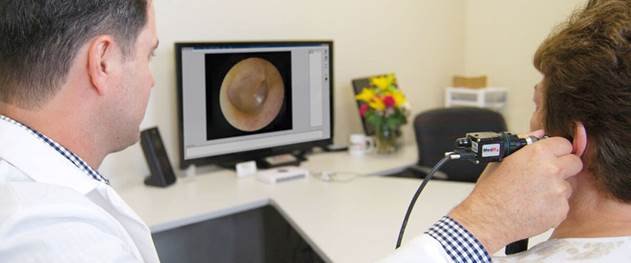
At OPERA hearing centers, a hearing specialist examines the patient’s ear canal and eardrums by the modern equipment – video otoscopy. Video otoscopic examination involves using an instrument called an otoscope to look inside the ear. An otoscope transmits a bright light into the ear canal and has a tiny video camera which relays images to a TV screen. Client can see the view on video screen display. During the video otoscopy, we can capture and print digital images of anything we find within the ear canal.
An audiometer is used to determine a person's hearing sensitivity at different frequencies. Hearing sensitivity is checked by the air conduction and bone-conduction testing. Air conduction testing is performed in the sound booth using either speakers, headphones, or insert earphones. The signal travels through the air in the outer ear to the middle ear and then to the cochlea in the inner ear. In bone-conduction testing, instead of using an earphone, a bone sensor is placed before the ear on the skull. This allows for stimulation of the cochlea via mechanical vibration of the skull with almost no stimulation of the outer and middle ear. During the test different intensities of sounds, tones and a certain frequency range: from low to high (250Hz, 500Hz, 1000Hz, 2000Hz, 4000Hz, 8000Hz) are used.
Standard methods are used to determine the sensitivity of the hearing. The results of Your hearing tests are mapped onto a chart called an audiogram, which gives a visual overview of Your hearing loss and its impact on Your everyday life. Reliable hearing assessmement provides You a lot of information about ear disease.
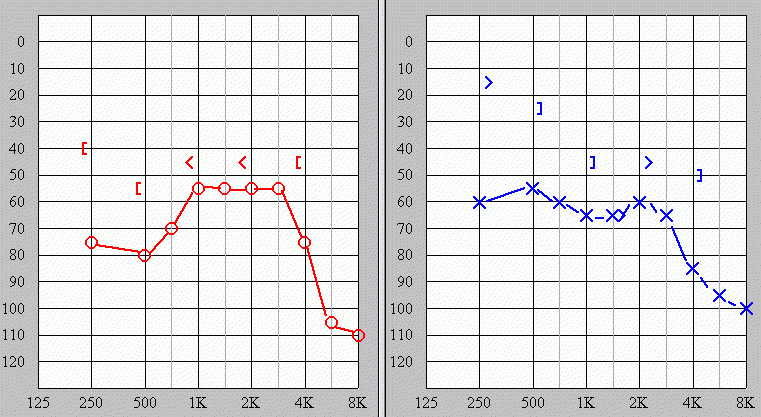
The example of audiogram