Klausa – Jūsų esminis turtas
Klausa – vienas svarbiausių pojūčių, padedančių žmogui bendrauti, orientuotis aplinkoje ir saugiai gyventi.
Tinkamai veikianti klausa leidžia atpažinti balsus, garsus, muziką, įspėjimus – todėl svarbu rūpintis savo klausos sveikata laiku.

Kaip mes girdime?
Pagrindiniai klausos sutrikimų tipai
Kondukcinis
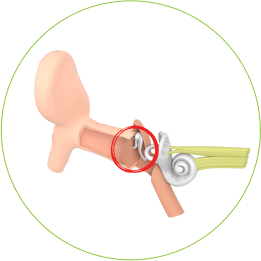
Laidumo sutrikimas atsiranda tada, kai garsas negali tinkamai patekti iš išorinės ar vidurinės ausies į vidinę ausį.
Neurosensorinis

Neurosensorinis (jutiminis) sutrikimas pasireiškia, kai pažeidžiami klausos nervai ar vidinė ausis, atsakingi už garso perdavimą į smegenis.
Mišrus
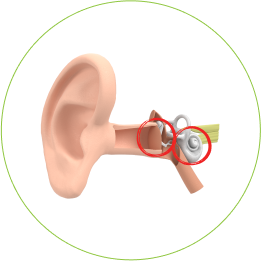
Mišrus klausos sutrikimas – tai laidumo ir neurosensorinio sutrikimų derinys. Tokiu atveju pažeidimai nustatomi keliose klausos sistemos dalyse.
Situacijos
Dažniausios klausos sutrikimo priežastys
Klausos sutrikimas gali būti:
Įgimtas – nustatomas nuo gimimo arba ankstyvoje vaikystėje.
Įgytas – išsivysto vėliau dėl išorinių ar vidinių veiksnių.
Svarbu žinoti: Senėjant, visi pojūčiai silpnėja, įskaitant ir klausą. Todėl dauguma neprigirdinčių asmenų – tai vyresnio amžiaus žmonės, kuriems klausos silpnėjimas yra natūralus senėjimo procesas.
Priežastys, galinčios lemti klausos silpnėjimą ar praradimą:
- Senėjimas
- Infekcijos, virusinės ligos
- Apsinuodijimas cheminėmis medžiagomis (intoksikacija)
- Ausų traumos ar mechaniniai sužalojimai
- Ilgalaikis poveikis stipriam triukšmui
- Vitaminų trūkumas
- Vidaus organų ligos (širdies, inkstų, kraujotakos sutrikimai)
- Nervų sistemos ligos (išsėtinė sklerozė, encefalitai, aterosklerozė ir kt.)

Kaip atpažinti klausos sutrikimus?
Klausos sutrikimai dažnai vystosi palaipsniui, todėl juos sunku pastebėti ankstyvoje stadijoje. Vis dėlto, kuo anksčiau jie atpažįstami, tuo didesnė tikimybė užkirsti kelią tolimesniam klausos blogėjimui ir pagerinti gyvenimo kokybę.
Dažniausi klausos sutrikimų požymiai
Svarbu: klausos sutrikimas gali paveikti vieną arba abi ausis, būti laikinas arba nuolatinis – todėl svarbu jį pastebėti kuo anksčiau.
Jeigu pastebite vieną ar kelis iš šių simptomų, tai gali būti pirmieji klausos sutrikimo signalai:
- Dažnai prašote pakartoti tai, kas buvo pasakyta;
- Garsinate televizorių ar radiją labiau nei anksčiau;
- Jums sunku girdėti pokalbius triukšmingoje aplinkoje (pvz. restorane ar prekybos centre);
- Atrodo, kad žmonės šneka neaiškiai arba „murma“;
- Vengiate telefoninių pokalbių dėl prasto girdimumo;
- Pastebite švilpimą ar ūžesį ausyse (tinnitus);
- Aplinkiniams atrodo, kad reaguojate lėčiau arba neįprastai;
- Vaikams: neatsiliepia į garsus, sunkiai suvokia kalbą, lėčiau vystosi kalbiniai įgūdžiai.
Rūpinkitės savo klausa – nedelskite
Jeigu pastebėjote galimus klausos sutrikimo požymius sau ar artimajam, nedelskite. Kuo anksčiau bus nustatyta diagnozė, tuo veiksmingesnė bus pagalba.
Užsiregistruokite klausos patikrai jau šiandien!

Kaip atliekamas klausos tyrimas?
Klausos tyrimas – tai saugus, neskausmingas ir tikslus būdas įvertinti klausos būklę.
Rekomenduojama pasikonsultuoti su ausų, nosies ir gerklės gydytoju (LOR) arba klausos specialistu (audiologu), jei:
- Ausų apžiūra su videootoskopu
- Prieš tyrimą klausos specialistas apžiūri ausų landas ir būgnelius modernia kamera, kurios vaizdą matote ekrane – viskas aišku ir vizualu.
- Audiometrija – klausos tikrinimas:
- Orinis laidumas – naudojamos ausinės.
- Kaulinis laidumas – naudojamas specialus kaulinis daviklis už ausies.
- Naudojami skirtingo intensyvumo ir dažnio garsai (250 Hz–8000 Hz).
- Audiograma – rezultatai grafiškai pateikiami audiogramoje, leidžiančioje tiksliai įvertinti klausos jautrumą.
Kuo skiriasi Audiologinis klausos tyrimas ir klausos testas
Profesionalus klausos tyrimas (audiograma).
Internetu atliekamas testas nenurodo tikslios diagnozės. Jis gali būti pirmas žingsnis apsispręsti ar jau laikas užsirašyti profesionaliai klausos patikrai. Jo metu Jūs sužinosite:
- Jūsų klausos jautrumą skirtingų dažnių garsams,
- Įvertinamos abiejų ausų ypatybės,
- Pateikiamos rekomendacijos, bet nėra nurodoma tiksli diagnozė.


Klausos reabilitacijos būdai
Klausos reabilitacija – tai individualiai pritaikytų sprendimų kelias į geresnį girdėjimą. Didžiajai daliai klausos sutrikimų taikoma reabilitacija klausos aparatais.
Tačiau, būna ligų, kurioms taikomi kiti metodai: operacijos ar medikamentinis gydymas. Būtina kreiptis į gydytoją, kad būtų nustatoma tiksli diagnozė.
